Linear rails with a square section, such as Hiwin guideways, are the first choice when accuracy and reliability are needed. They are the standard on CNC machines and have been gaining popularity in hobby 3D printers and laser cutters as well.
Let’s see what kinds of rails are out there, how to choose the right type, and how they compare to other motion systems like V-wheels and smooth rods.
What are linear rails?
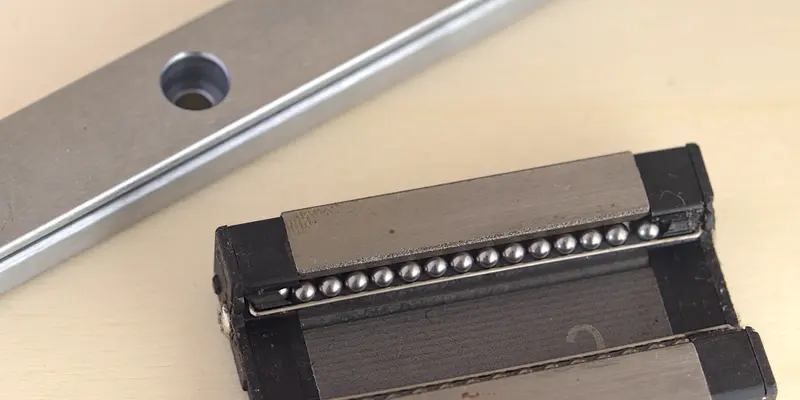
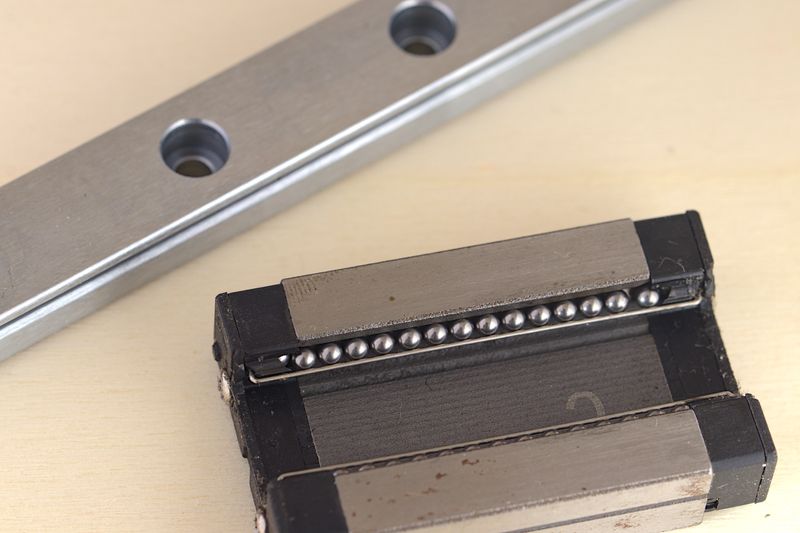
Linear rails are made of precision ground steel, and allow a carriage to travel along its length. Crucially, they constrain motion along all axes except the axis of movement. The carriage cannot tilt up/down or sideways, or roll around the rail.
The carriages make contact with the rail using recirculating balls, much like the linear bearings designed for smooth rods, but have much tighter tolerances which results in less play.
Linear rails and carriages have been prohibitively expensive for a long time, but in recent years their price has fallen considerably.
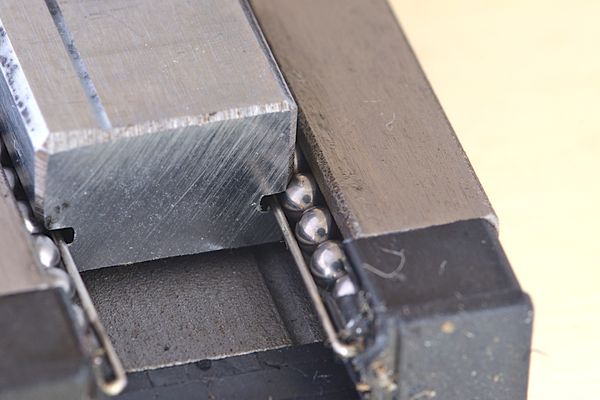
An MGN12 carriage uses recirculating balls to slide across a steel rail.
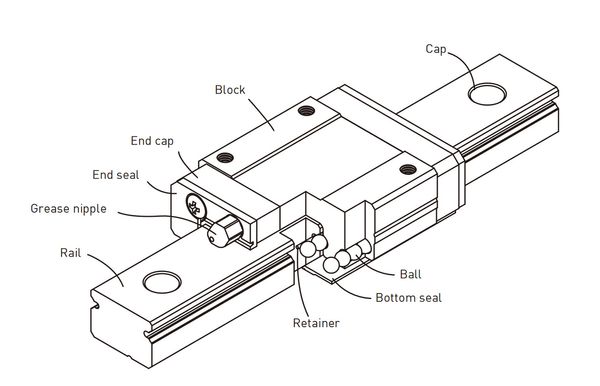
Hiwin MGN12 rail and carriage (image source)
What’s Hiwin?
MGN9, MGN12, and other rail names are all part of Hiwin’s naming system. This is a name you’re bound to come across when researching linear rails. Hiwin is a popular Taiwanese producer of linear motion components. Due to the popularity of Hiwin rails, many Chinese manufacturers have been making their own products following Hiwin specs, including sizes and model names.
This makes it easy to shop for cheap Chinese rails as long as you’re familiar with Hiwin’s naming system (as described in their catalogue ).
Other manufacturers include IKO , THK and NSK . Their rails can be found on eBay quite easily, with NSK being the most expensive of the three.
Linear rails vs V-wheels
V-wheels are the main alternative to linear rails in the hobby space, and are widespread in 3D printers and budget laser cutters (like some variants of the K40 laser cutter). V-wheels are designed to ride on V-shaped grooves of aluminum extrusions. Because of this, they are extremely cost effective for large machines since parts of the frame also act as linear guides.
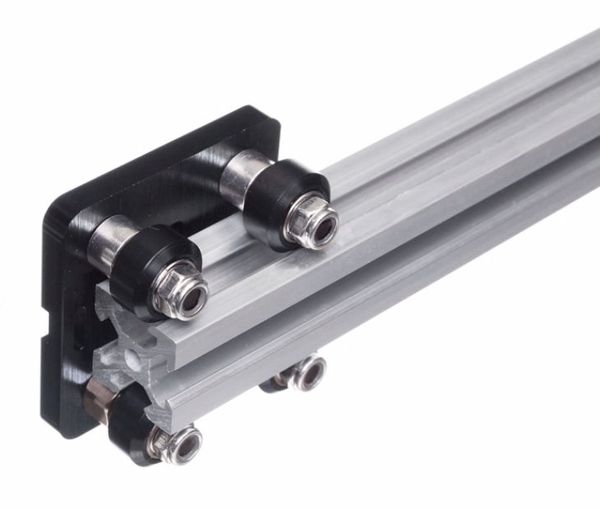

However, V-wheels need to be carefully tightened with a small wrench, and require maintenance as they loosen and wear out over time. V-wheels are very much a “save now, worry later” solution. Still, when properly installed, they do provide good accuracy.
Tip: three-wheel gantries are preferred over four-wheel gantries to avoid overconstraint issues.
Linear rails vs smooth rods
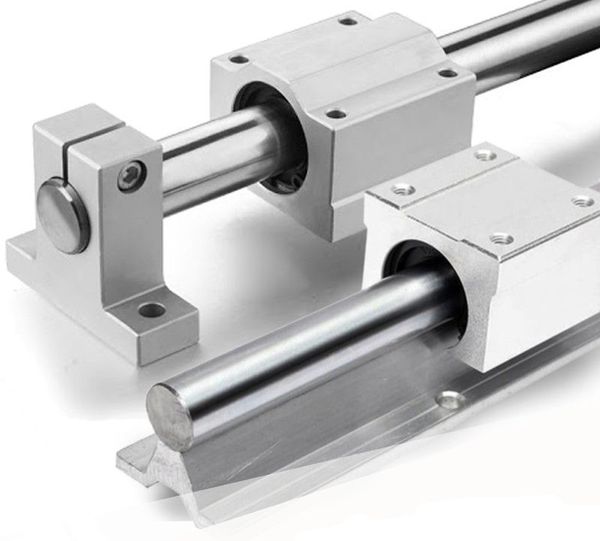

Unsupported and supported smooth rods made of ground steel.
If you compare smooth rods to linear rails side-by-side, the first thing you’ll notice is their play, or rather clearance, as linear bearings designed for smooth rods tend to be fit quite loosely. This makes them particularly poor at withstanding loads that cause the bearing to “yaw” or tilt perpendicularly to the axis of travel. This is why they are rarely used outside of low-load applications like 3D printers and laser cutters.
On the other hand, linear rail carriages are designed to have raceways with slightly oversized balls. This “negative clearance” is known as preload.
Preload is measured relatively to C, which is the dynamic load rating (more on this later).
| Class | Hiwin code | Preload | Condition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Very light | Z0 | 0 ~ 0.02C | Certain load direction, low impact, low precision required |
| Light preload | ZA | 0.03 ~ 0.05C | low load and high precision required |
| Medium preload | ZB | 0.06 ~ 0.08C | High rigidity required, with vibration and impact |
The other issue with smooth rods is deflection, which is how much the rod bends when a load is applied. Deflection is the main weakness of unsupported rods, and the reason why supported rods are always preferable for moderate and heavy load applications.
MGN vs HGR linear rails
Let’s take a look at Hiwin rails, and by extension the many inexpensive Chinese clones available. There are many different series of rails and carriages, but the two most popular ones by far are the MGN and HG series. MGN carriages feature two bearing raceways, while the HG series goes up to four which provides lower friction.
MGN linear rails are best suited for low load applications, such as 3D printers, pick and place machines, and pen plotters. However they have can also be used in budget CNC machines like the RigCNC
Load ratings
Linear rails are designed to resist multiple kinds of radial loads, which are forces perpendicular to the direction of movement:
- Static load (C0) is the maximum load before the bearings or raceways are permanently deformed.
- Dynamic load (C) is the maximum continuous load applied to the bearings and raceways that doesn’t compromise the service life of the rails beyond the nominal rating (which is 50km for MGN/HG rails and other ball-type rails).
- Moment load is a load that can cause a rotation of the bearing around one of three axes: pitch (front/back tilt), yaw (sideways rotation), and roll (rotation around the axis of motion).
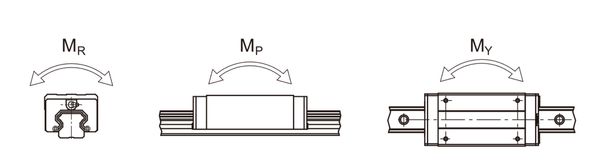
Three types of moment load: roll, pitch and yaw (source: Hiwin)
Below are two tables with Hiwin’s load ratings of the most common models of carriages:
- Static and dynamic loads are indicated in kN (1 kiloNewton = 102 kg or 224.8 lb of force)
- Moment loads are indicated in Newton-meter. 1 N-m is equivalent to 141.6 oz-in.
Also keep in mind that these figures are for single blocks only.
Load ratings: MGN series
- C: short MGN blocks
- H: standard length MGN blocks
Load ratings: HG series
- HGW: wide flanged blocks
- HGH: narrow and shorter blocks without flanges
Hiwin MGN series: MGN9, MGN12, MGN15
The naming of MGN rails is straightforward, with the number in MGN9/MGN12/MGN15 indicating indicating the rail width in mm. MGN carriages are available in two lengths:
- C (short)
- H (standard length)
The hole spacing also changes depending on the length.
Weight
Weight is a big consideration whenever a linear rail is mounted onto a gantry. High mass means lower possible acceleration, is undesirable. Each tier of MGN rails almost doubles the weight:
| Rail size | Rail weight | Carriage weight |
|---|---|---|
| MGN9 | 380 g/m | 26 g |
| MGN12 | 650 g/m | 54 g |
| MGN15 | 1060 g/m | 92 g |
Carriage width
It’s worth noting that MGN9 carriages are the only ones out of the three sizes that do not overhang a 2020 extrusion. This means that the carriage can ride right next to a panel, or that two MGN9 rails can be mounted 90 degrees apart onto the same 2020 extrusions like this:
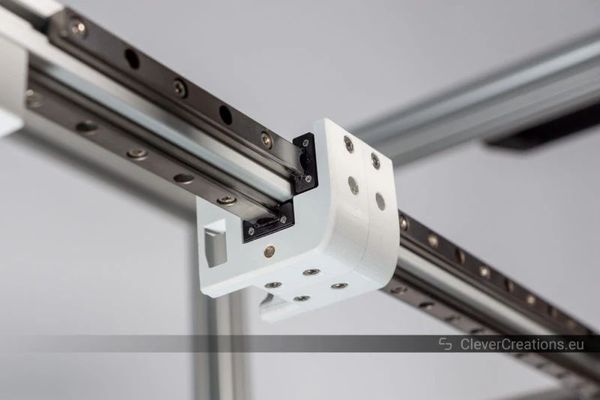

Thanks to their narrow width, MGN9 carriages can be mounted in pairs like this (image source)
Comparison table: MGN series
Hiwin HG (HGR) series: HGR, HGW, HGH, HGL
As mentioned before, HG carriages are taller to accomodate four raceways instead of two on the MGN series. This makes them a good choice for heavy load applications like CNC milling, and according to Hiwin it also makes them suitable to be mounted onto slightly uneven surfaces. The open-source PrintNC CNC router design takes advantage of this by using HGR rails on rectangular steel tubes instead of aluminum extrusions.
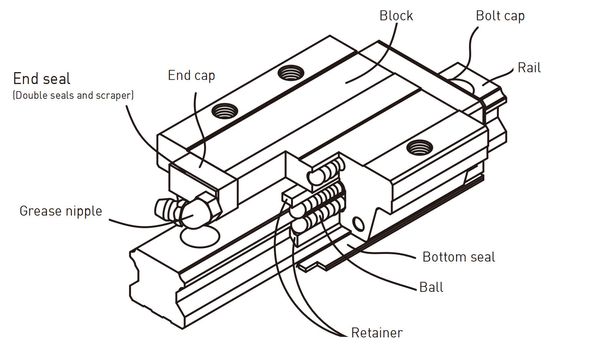
HG nomenclature
HGR and other HG rails/carriages have a more convoluted naming scheme, with lots of variants.
- HGR is the rail only.
- HGW are carriages with flanges and wider hole spacing.
- HGH are carriages without flanges, taller than HGW.
- HGL are carriages without flanges, as tall as HGW.
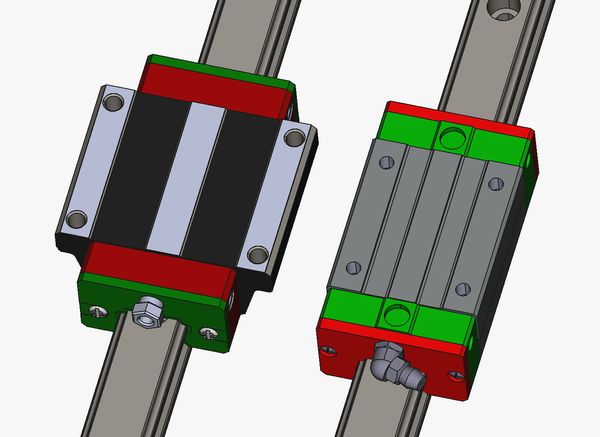
HGW vs HGH carriage
Carriages will usually be listed as CA, CC, HA, or HC.
- CA carriages have blind tapped holes, so they can only be bolted from the top.
- CC carriages have through holes, so they can be bolted from either direction.
- HA and HC are longer in order to support heavier loads. These longer blocks are hard to find online, unlike MGN-C blocks.
- (As a side note, there are also CB and HB blocks, where the B indicates they are bolted from the bottom, but they not easily available.)
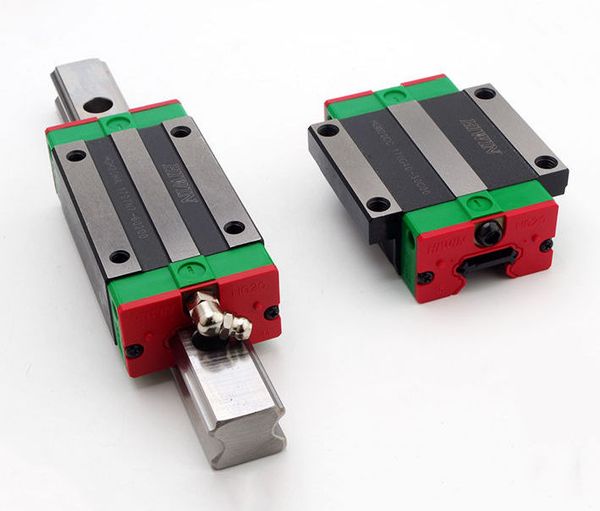

An extra-long HGH-HA block vs a standard length HGW-CC (flanged) block.
The flanges on HGW blocks usually allow for through holes, which is why basically all HGW carriages are HGW-CC, whereas all HGH carriages are HGH-CA. Well, Hiwin does list HGW-CA carriages, which can only be bolted from the top, but I’ve never seen them sold (at least as clones) online.
Therefore, it’s safe to ignore the last two letters.
All HG carriages have a grease nipple, which allows lubricant to be easily squeezed into the raceways. Hiwin recommends checking the lubricant every 100 km or every 3-6 months.
- HGW (flanged) carriages can withstand moment load better (i.e. a load that would cause a rotation), as they are shorter and the bolts are more widely spaced.
- HGH (square) carriages have the advantage of being more compact.
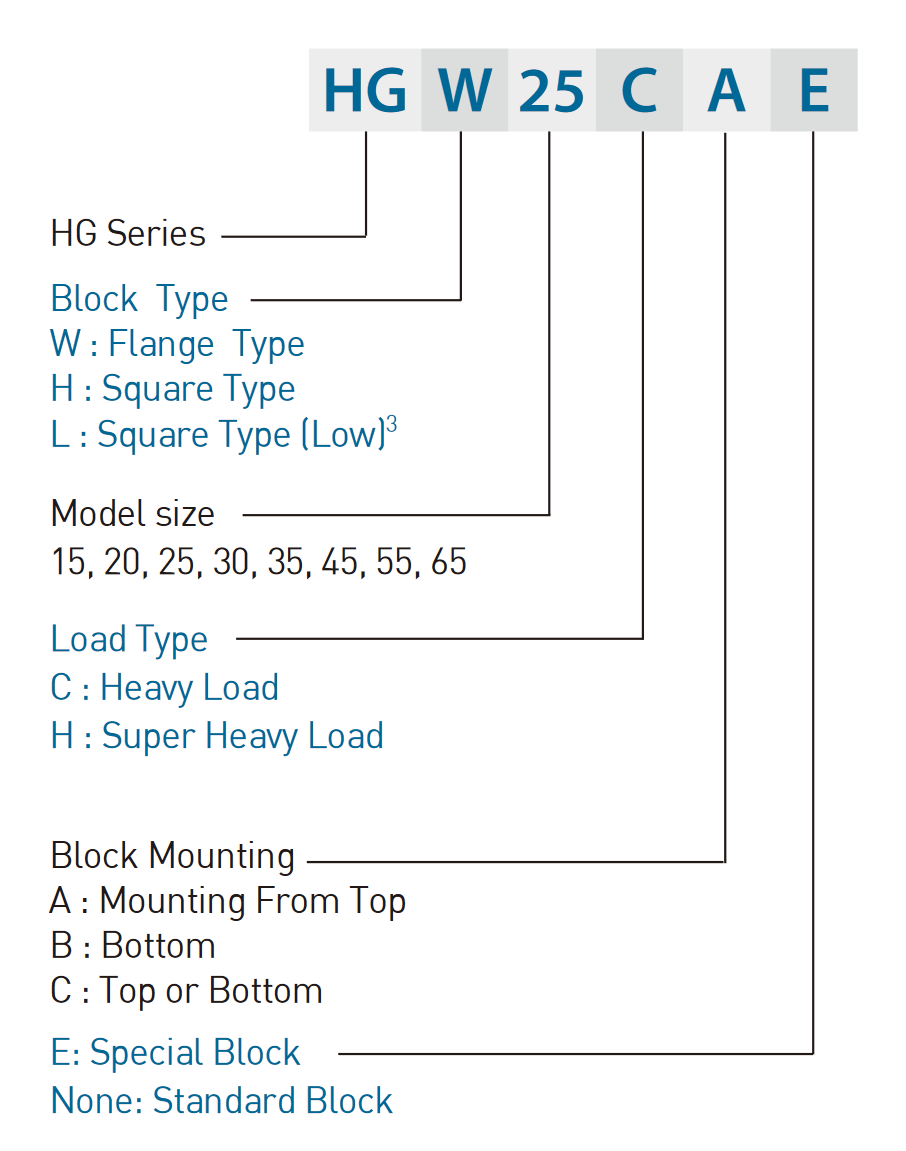
The naming scheme for HG series rails (source: Hiwin)
Comparison table: HG series
Note: I have only included specs for the short CA/CC carriages, as the HA/HC carriages are much harder to find online.
Tips on buying, using & maintaining linear rails
Handling
Be careful when sliding a carriage off a rail! The balls inside linear rail blocks can very easily fall out of their raceways when removed.
If you need to remove a block for maintenance, slide it off slowly over a bowl or tray.
If you only need to remove the block and not access the raceways, slide the block from one rail to another or into the plastic rail that blocks sometimes come with.
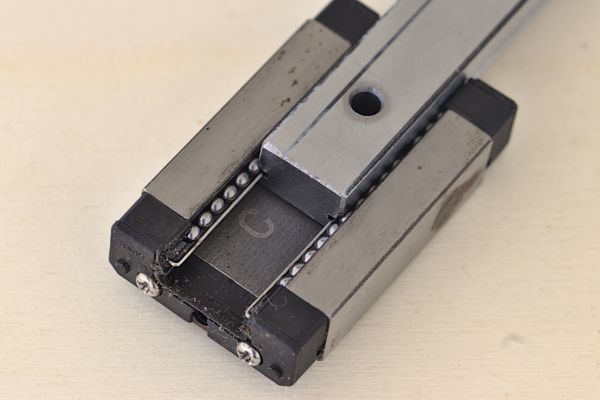

Take care when removing a carriage from its rail. To prevent the steel balls from coming off, it's best to hold the carriage in place and slide the rail off the block.
Cleaning
Linear rails you receive will probably be sticky. You may think it’s lubricant, but instead it’s anti-rust grease. They can be cleaned by submerging them in isopropyl alcohol after disassembly.
Installation
MGN and HG linear rails can be installed in any orientation, due to the design of their raceways.
When mounting linear rails to 2020 (or 2040, etc…) aluminum extrusions, it’s important to use the right bolts:
| Rail size | Bolt size |
|---|---|
| MGN9 | M3 x 8 mm |
| MGN12 | M3 x 8 mm |
| MGN15 | M3 x 10 mm |
| HGR15 | M3 x 10 mm |
I recommend using square slider nuts to secure MGN rails to 2020 extrusions, as long as you have access to at least one end of the T-slot. Otherwise, drop-in T-nuts are very convenient but you run the risk of accidentally tightening the nut against the rail itself, without the nut flanges engaging the 2020 profile.
Lubrication
Lithium-based grease is often recommended for linear rails.
According to Hiwin’s official lubricating instructions , these are the recommended grease lubricants for standard applications:
| Manufacturer | Grease |
|---|---|
| HIWIN | G05 |
| Klüber | Klüberlub GL-261 |
| Mobil | Mobilux EP1 |
| Fuchs | Lubritech Lagermeister BF2 |
| Lubcon | TURMOGREASE CAK 2502 |
These are Hiwin’s recommended oil lubricants:
| Manufacturer | Oil |
|---|---|
| Klüber | Klüberoil GEM 1-150 N |
| Mobil | Mobilgear 630 |
| Fuchs Lubritech | GEARMASTER CLP 320 |